GitHub Workflows¶
The exasol-toolbox ships with various GitHub workflow templates. To leverage the full feature set of the toolbox, you should use them.
Attention
Generally, it is advised to install/use all workflows provided by the toolbox as a whole due to their interdependencies.
However, if you know what you are doing and are well-versed in GitHub workflows and actions, you can use just select individual ones or use them as inspiration. Still, an individual approach is likely to be more error-prone.
Note
The toolbox command itself, tbx, provides various CLI functions to help you maintain those workflows.
For further help, run the command tbx workflow --help.
1. Configure the GitHub project¶
Make sure your GitHub project has access to a deployment token for PyPi with the following name: PYPI_TOKEN. It should be available to the repository either as an Organization-, Repository-, or Environment-secret.
If your CI workflow involves slow or expensive steps you can guard these to be executed only after manual approval. The CI workflow will automaticall create a GitHub environment named
manual-approval. You only need to add reviewers in (Settings/Environments/manual-approval) and move the steps to be guarded into the related section in jobslow-checksin file.github/workflows/merge-gate.yml.
2. Add all workflows to your project¶
tbx workflow install all
Warning
If you already have various workflows, you may want to run the
updatecommand instead of theinstallcommand.Some workflows depend on other workflows. Please ensure you have all the required workflows if you do not install all of them.
3. Update Branch Protection¶
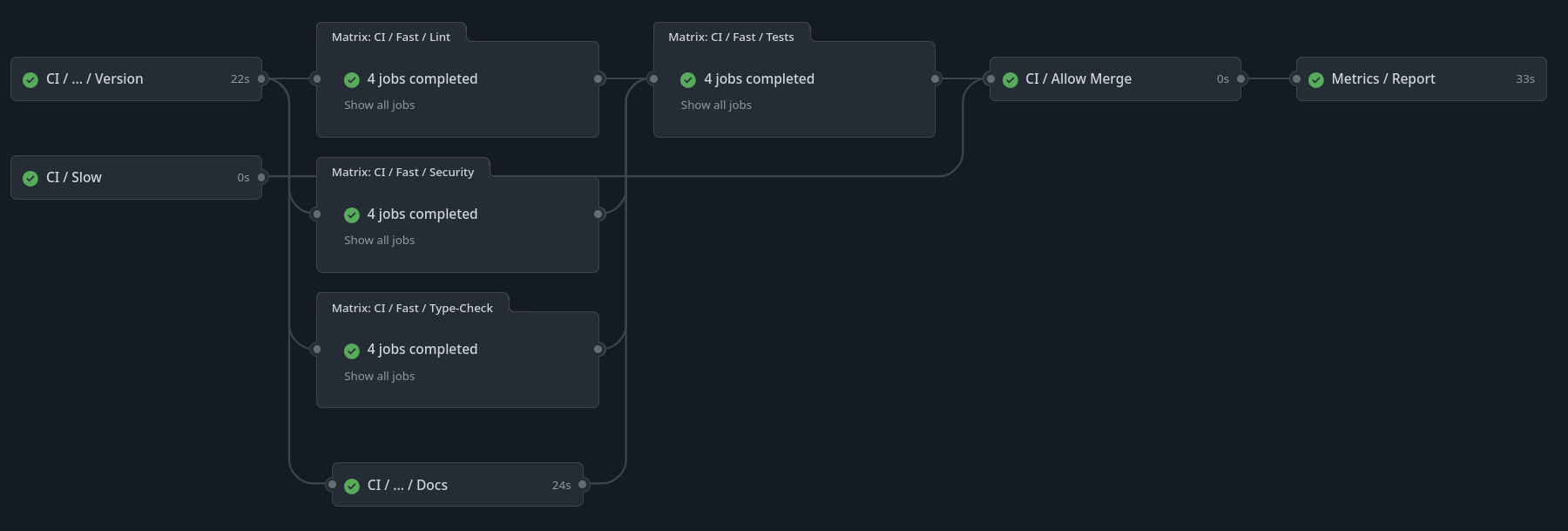
The best and most maintainable way to have solid branch protection (Settings/Branches/main) is to require the workflow CI / Allow Merge to pass successfully.
Note
Setting the required status checks to pass before merging is only possible after running a CI build at least once on the affected branch.